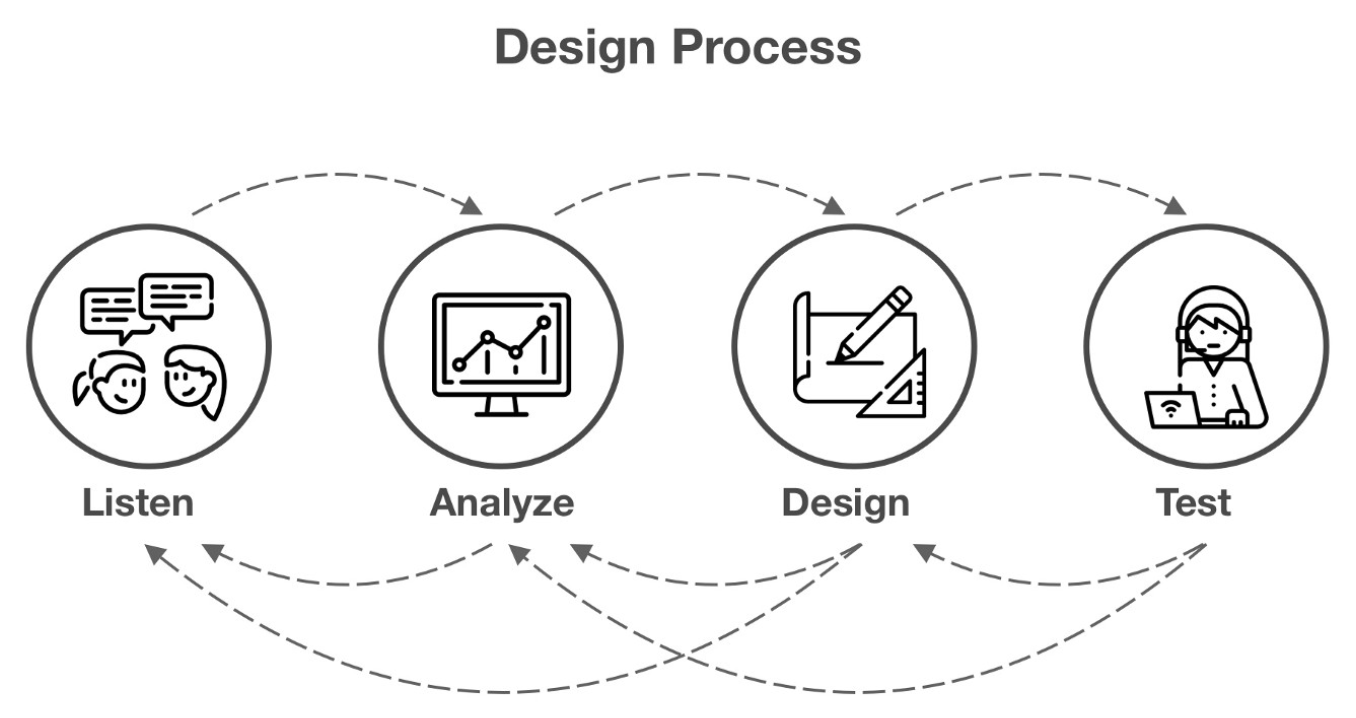
Design Process
The design process is a step-by-step approach used by designers to ensure that they produce the most effective design. It involves thinking, discussion, research, analysis, problem solving and developing ideas. This is the foundation work required for an effective design solution.
It is important to note that the design process is not strictly linear.
Design thinking process
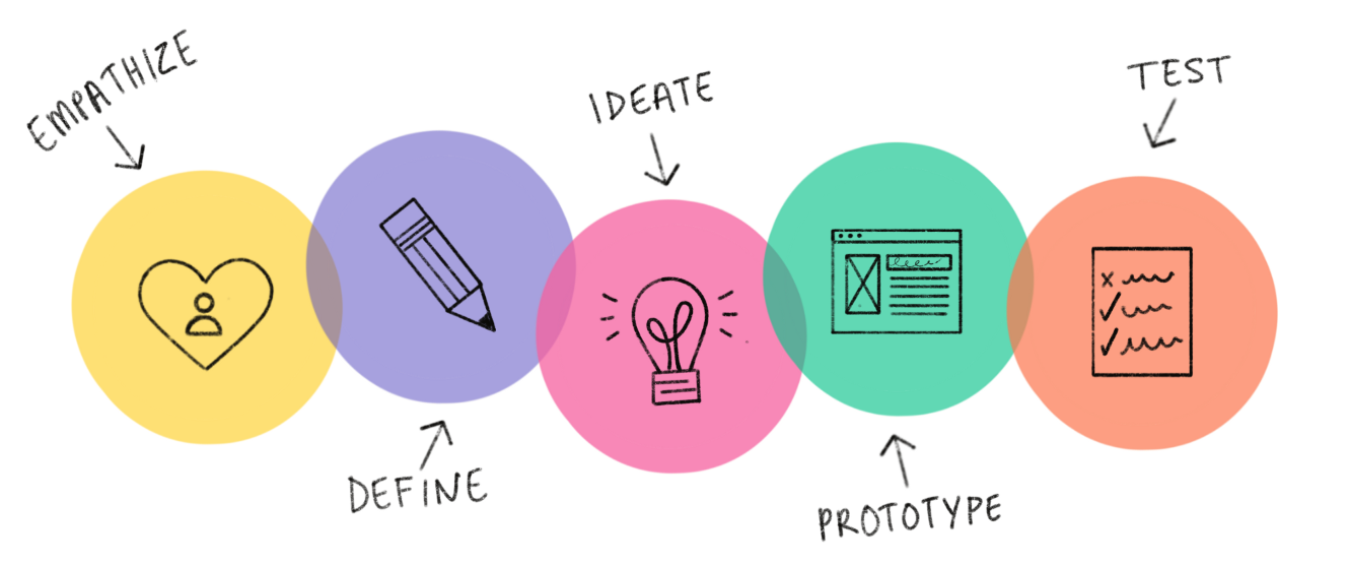
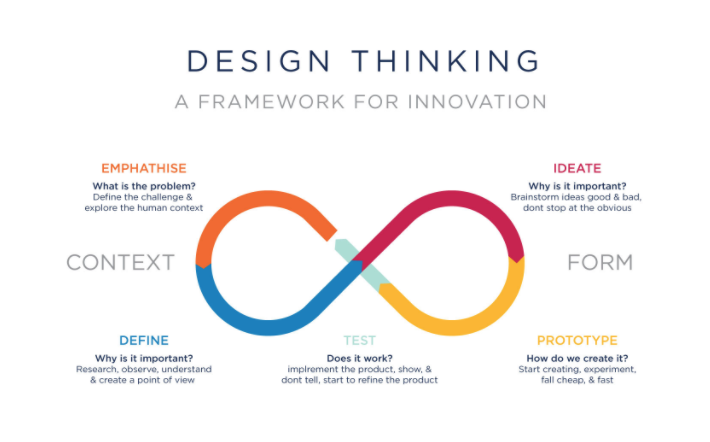
Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process which seeks to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. The method consists of 5 phases—Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test and is most useful when you want to tackle problems that are ill-defined or unknown.
Stage 1: Empathize – Research Your Users' Needs
The first stage of the design thinking process allows you to gain an empathetic understanding of the problem you’re trying to solve, typically through user research. Empathy is crucial to a human-centered design process like design thinking because it allows you to set aside your own assumptions about the world and gain real insight into users and their needs.
Stage 2: Define – State Your Users' Needs and Problems
In the Define stage, you accumulate the information you created and gathered during the Empathize stage. You analyze your observations and synthesize them to define the core problems you and your team have identified so far. You should always seek to define the problem statement in a human-centered manner as you do this.
Stage 3: Ideate – Challenge Assumptions and Create Ideas
Designers are ready to generate ideas as they reach the third stage of design thinking. The solid background of knowledge from the first two phases means you can start to “think outside the box”, look for alternative ways to view the problem and identify innovative solutions to the problem statement you’ve created.
Stage 4: Prototype – Start to Create Solutions
This is an experimental phase, and the aim is to identify the best possible solution for each of the problems identified during the first three stages. Design teams will produce a number of inexpensive, scaled-down versions of the product (or specific features found within the product) to investigate the problem solutions generated in the previous stage.
Stage 5: Test – Try Your Solutions Out
Designers or evaluators rigorously test the complete product using the best solutions identified in the Prototype phase. This is the final phase of the model but, in an iterative process such as design thinking, the results generated are often used to redefine one or more further problems. Designers can then choose to return to previous stages in the process to make further iterations, alterations and refinements to rule out alternative solutions.
https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/design-thinking
learning objectives
Level 4
- Describe key stages in the design process.
- Create work that satisfies individually, key stages in the design process.
Interactions, engagements and activities
Activities that require learners to brainstorm multiple solutions to the same problem are a great way encourage idea generation.
Level 5
- Plan the the application of a design process, identifying key milestones and expected time spent at each stage.
- Produce work that appropriately meets the requirements of each stage of a design process.
- Use an iterative approach to a design process
Interactions, engagements and activities
Activities that encourage learner to work through multiple stages of a design process.
Level 6
- Document own design process and apply it while creating design work.
- Compare differing processes and evaluate their effectiveness.
- Create design briefs.
- Describe a range of methodologies, mindsets, systems or procedures that can be applied to a design process. (Human centred, User experience, Agile, Lean)
- Use project management techniques and tools to work collaboratively. (Kanban, trello, Scrum)
Interactions, engagements and activities
Describe the types of interaction and activities that could help achieve the objectives.
No comments to display
No comments to display